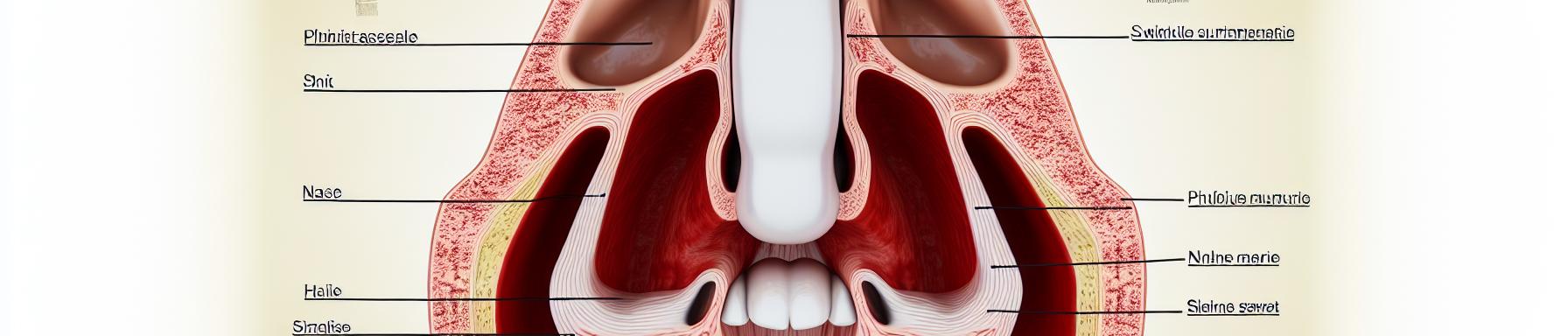
Rhinitis can be caused by a variety of factors, and is an acute or chronic inflammatory disease that mainly affects the lining of the nasal cavity. Depending on the case, rhinitis can be caused by allergens, i.e. substances that can cause allergic reactions in the body, or by pathogens such as a virus or bacteria. It is interesting to know that allergic rhinitis is a pathology that is generally much more widespread than infectious rhinitis. Sometimes seasonal, it unfortunately very often proves to be persistent, disrupting the lives of all those who suffer from it in a considerable way. Also known as hay fever or pollinosis, seasonal allergic rhinitis manifests itself mainly under the influence of pollen, and more particularly that of grasses.
Persistent allergic rhinitis, on the other hand, is somewhat different, as it is attributable to a number of allergenic agents such as dust, animal hair, dust mites or even pollution. If we call this form of rhinitis persistent, it is because, unlike seasonal rhinitis, it does not manifest itself at a specific time of the year but rather every time the body is confronted with the allergen to which it is sensitive. In short, for reasons that medicine still knows little about, the body of subjects prone to allergies develops at one time or another a hypersensitivity to a normally harmless foreign substance. Once hypersensitivity has been acquired, the allergy then results in an immediate reaction such as rhinitis as soon as the subject finds himself in the presence of the substance to which he has developed an intolerance.
Although allergic rhinitis is a priori benign, it seems that it can eventually promote the appearance of more serious respiratory pathologies such as asthma. Therefore, it is much better not to neglect the symptoms and to treat them appropriately, especially when the affected subjects are young children. In conventional medicine, allergic rhinitis is most often treated with antihistamines and decongestant substances. Infectious rhinitis, which, it should be remembered, occurs following viral or bacterial attacks, is the subject of treatments aimed at eliminating the pathogen responsible for the disease.
While homeopathy does not claim to cure rhinitis, it can nevertheless alleviate the symptoms and provide significant relief to those who suffer from it. It has no side effects and is also much gentler than conventional treatments, which can sometimes lead to drowsiness and other side effects. In addition, some research on specific homeopathic remedies has shown that the substances studied may promote desensitization in allergic subjects, i.e., a decrease in the sensitivity of their bodies to the allergenic agents involved.
Symptoms
When inflammation occurs, it is always accompanied by more or less severe nasal congestion, repeated sneezing and nasal discharge that is often watery. In some forms of allergic rhinitis, these symptoms can be associated with burning sensations in the nasal cavities, as well as itching in the palate and tearing that can be very severe. If it is persistent, allergic rhinitis can also cause difficulty concentrating in affected subjects. Infectious rhinitis, on the other hand, is mainly characterized by frequent sneezing accompanied by watery or purulent nasal discharge. In addition to these symptoms, there may also be a feeling of nasal obstruction, as well as pain in the maxillary and frontal bones. In addition, it is important to know that in some cases, infectious rhinitis can result in sinusitis.
Treating seasonal or persistent allergic rhinitis
In order to reduce the swelling of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavities and the feeling of discomfort related to discharge, it is advisable to take 5 granules of Apis mellifica 15 CH as well as 5 granules of Arsenicum album 9 CH three times a day as soon as the first sneezing and discharge appear.
If the nasal congestion and discharge are accompanied by itching on the palate, then 5 granules of Sabadilla 15 CH should be taken three times a day, from the beginning of the attack. In the event that pruritus is associated with other itching in the ears, it is advisable to take 5 granules of Arundo donax 5 CH three times a day, as soon as the first symptoms appear.
In the case of seasonal allergic rhinitis, it will be possible to take 5 granules of Histaminum 9 CH or 5 granules of Lung Histamine 9 CH twice a day from the beginning of the season in which the allergy usually occurs. In some cases, it will also be possible to take 5 granules of Pollen 30 CH per day for as long as the season conducive to the allergic reaction lasts. Nevertheless, it is preferable in these circumstances to let the practitioner establish the appropriate treatment and dosage according to the symptoms.
Sometimes, depending on the disorders with which they are associated, seasonal or persistent allergic rhinitis must also be treated more specifically with remedies such as Allium cepa, Ambrosia artemisiaefolia, Kalium iodatum or Naphtalitum.
Limiting the recurrence of allergic rhinitis
It is important to know that it is extremely difficult to permanently cure seasonal and persistent allergic rhinitis once it appears. Nevertheless, thanks to homeopathy, it is still possible to significantly reduce the intensity of the symptoms they cause as well as recurrences. Consequently, the preventive remedies that are then suitable are most often remedies such as Lachesis mutus, Lycopodium clavatum, Natrum muriaticum, Nux vomica, Psorinum, Pulsatilla, Sulphur, Sulphur iodatum or Tuberculinum. But once again, it is important to remember that it is up to the practitioner to establish the most appropriate treatment according to the symptoms and the frequency of onset of the disease.
Treating infectious rhinitis with a watery nasal discharge
In case of watery nasal discharge, it is advisable to take 5 granules of Allium cepa 9 CH every hour if the rhinitis is accompanied by tearing and a tingling sensation in the eyes. Once symptoms have subsided, doses can then be reduced until total improvement is felt.
If the discharge is associated with nasal congestion, 5 Ammonium muriaticum 5 CH granules should be taken every hour until the obstruction gradually subsides. If the discharge is hot, it is advisable to take 5 granules of Arsenicum album 9 CH every hour or 5 granules of Kalium iodatum 9 CH if pain is noticeable in the maxillary and frontal bones. As far as these three remedies are concerned, it should be noted that the doses should also be reduced as the symptoms subside.
Treating infectious rhinitis with purulent nasal discharge
In the case of infectious rhinitis with purulent discharge, it is advisable to take 5 granules of Kalium bichromicum 9 CH three times a day until the discharge gradually decreases, as well as a dose of Hepar sulfuris calcareum 30 CH for four days. Once the symptoms have subsided, Kalium bichromicum should be taken less frequently.
It should also be noted that in some cases, remedies such as Ammonium carbonicum, Aralia racemosa, Arsenicum iodatum, Badiaga, Magnesia muriatica or Sambucus nigra may be recommended. Nevertheless, it will again be appropriate to let the practitioner decide on the most appropriate treatment according to various criteria that will allow him to establish his diagnosis.
Preventing recurrence of infectious rhinitis
As far as the preventive treatment of infectious rhinitis is concerned, the most appropriate remedies in this case are generally similar to those recommended for the prevention of allergic rhinitis. As a result, these treatments can also consist of remedies such as Lachesis mutus, Lycopodium clavatum, Natrum muriaticum, Nux vomica, Psorinum, Pulsatilla, Sulphur, Sulphur iodatum or Tuberculinum.
When to see a doctor?
If the rhinitis is caused by pathogens and is accompanied by purulent nasal discharge, it will be necessary to consult a doctor immediately so that he or she can initiate appropriate treatment. In addition, it is important to know that in the case of infectious rhinitis, homeopathy will only be used in addition to the prescribed allopathic treatment.
If the rhinitis is of allergic origin, it is best to consult a doctor as soon as recurrences appear so that he or she can determine which agents are responsible for the allergic reaction. In addition, it will be advisable to turn to a professional if the symptoms associated with the pathology are difficult to bear or if they cause many disorders.
Finally, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible if the affected person is very young (infant, child under two years of age, child) in order to avoid any risk of respiratory distress and to limit the future appearance of serious pathologies such as asthma.